Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (10): 1540-1546.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0713
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of Col-Tgel, a bioactive material, on human tissue stem cells
- State Key Laboratory of Experimental Hematology, Institute of Hematology and Blood Disease Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Tianjin 300020, China
-
Received:2017-11-13Online:2018-04-08Published:2018-04-08 -
Contact:Cheng Tao, Professor, State Key Laboratory of Experimental Hematology, Institute of Hematology and Blood Disease Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Tianjin 300020, China -
About author:Yin Xiu-xiu, Doctoral candidate, State Key Laboratory of Experimental Hematology, Institute of Hematology and Blood Disease Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Tianjin 300020, China -
Supported by:the National Key Research and Development Program of China, No. 2016YFA0100600; CAMS Initiative for Innovative Medicine, No. 2016-I2M-1-017; the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81400150, 81570164; the Science Foundation for Innovation Research Groups, No. 81421002; the Youth Foundation of PUMC and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, No. 3332016090
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yin Xiu-xiu, Hu Lin-ping, Zhu Cai-ying, Zhang Xiao-bing, Cheng Tao. Effects of Col-Tgel, a bioactive material, on human tissue stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(10): 1540-1546.
share this article
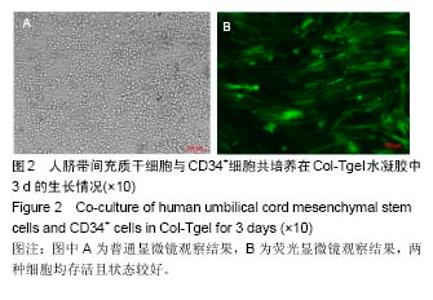
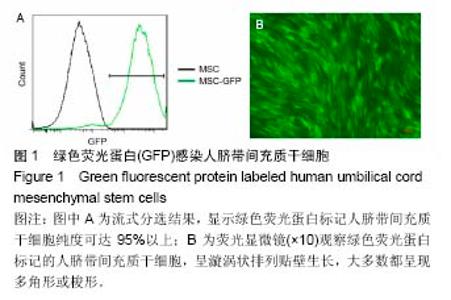
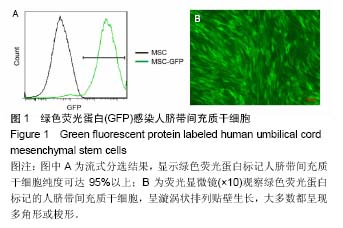
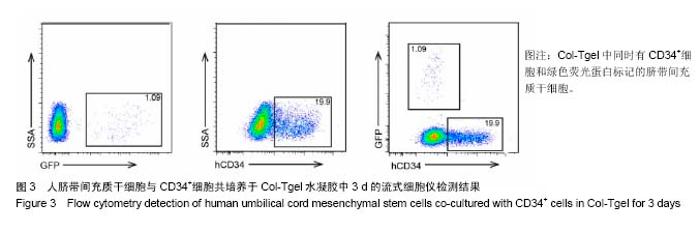
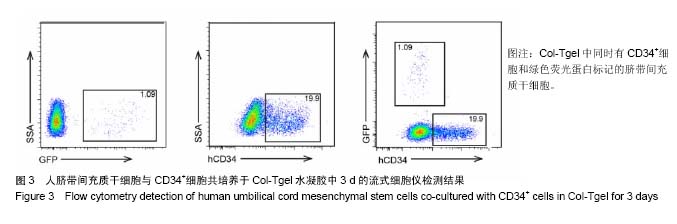
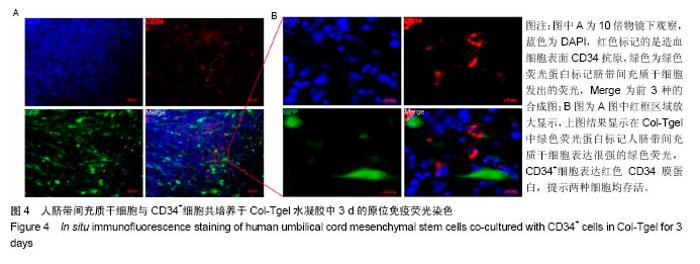
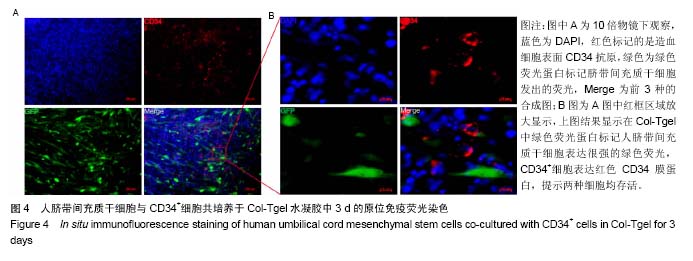
2.2 Col-Tgel对细胞体外培养活性的影响 三维培养组培养3 d后,显微镜下观察显示两种细胞均存活且状态较好(图2A),荧光显微镜下显示人脐带间充质干细胞发出绿色荧光(图2B)。用胰酶消化Col-Tgel中的细胞,标记表面人抗体CD34,流式检测结果显示,Col-Tgel中同时有CD34+细胞和绿色荧光蛋白标记的脐带间充质干细胞(图3),说明在体外Col-Tgel对人脐带间充质干细胞和CD34+细胞无毒性,两种干细胞均可在Col-Tgel中进行体外培养。原位免疫荧光染色进一步验证了该结果(图4)。以上研究结果表明,在体外培养中,Col-Tgel不影响人脐带间充质干细胞和CD34+细胞的活性。"
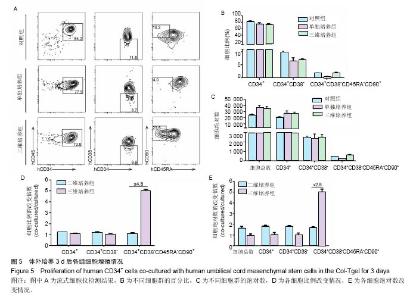
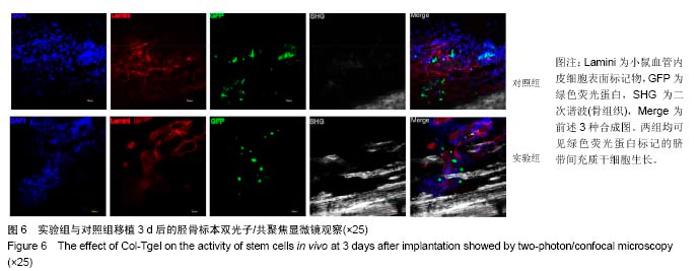
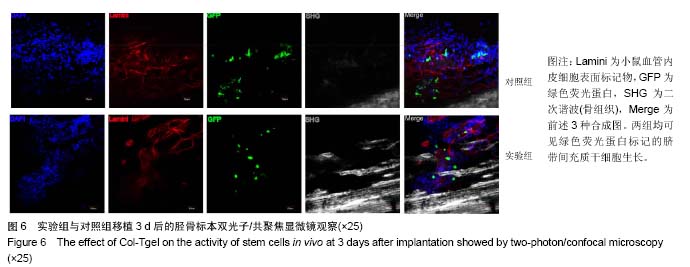
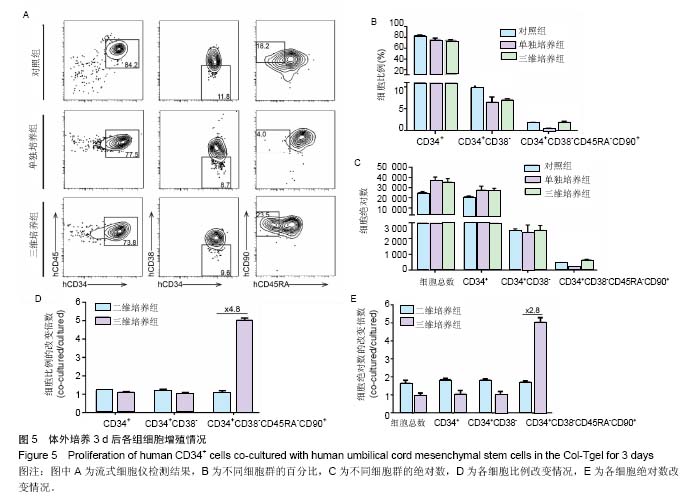
2.3 Col-Tgel在体外对人脐血CD34+细胞增殖的影响 单独培养组、三维培养组及对照组的CD45+CD34+细胞比例分别为(75.53±1.63)%、(74.40±0.38)%、(82.87±0.75)%,各组之间无差异(P > 0.05);CD34+CD38-细胞比例分别为(6.51±0.67)%、(7.08±0.07)%、(9.78±0.18)%,单独培养组及三维培养组均较对照组明显下降(P < 0.05);三维培养组CD34+CD38-CD45RA-CD90+细胞(长期造血干细胞)比例为(1.88±0.10)%,是单独培养组(0.32±0.11)%的5.9倍,但较对照组长期造血干细胞的比例增加不明显(图5A,B)。以上各组细胞的绝对数结果显示,三维培养组长期造血干细胞较单独培养组增加4.5倍,较对照组增加1.5倍(图5C),说明使用Col-Tgel对人脐带间充质干细胞和CD34+细胞进行共培养,可提高长期造血干细胞扩增数。三维培养组与单独培养组细胞总数、CD45+CD34+细胞扩增倍数和CD34+CD38-细胞扩增倍数在两种不同培养方式中并没有明显差异,但三维培养组长期造血干细胞的扩增倍数是二维培养组的2.8倍(图5D,E),说明相比于液体共培养,在Col-Tgel中人脐带间充质干细胞和CD34+细胞进行共培养更有利于长期造血干细胞的扩增。"
| [1]Orkin SH,Zon LI.Hematopoiesis: an evolving paradigm for stem cell biology.Cell.2008;132(4): 631-644.[2]Verfaillie CM.Hematopoietic stem cells for transplantation.Nat Immunol.2002;3(4):314-317.[3]Tan SL,Ahmad TS,Selvaratnam L,et al.Isolation, characterization and the multi-lineage differentiation potential of rabbit bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells.J Anat.2013;222(4): 437-450.[4]裴雪涛,杨莉,王洪欣,等.成人骨髓间充质干细胞体外扩增和定向诱导分化为骨和软骨细胞的研究[J].自然科学进展, 2001,11(10): 1062-1070.[5]Johansson CB,Momma S,Clarke DL,et al.Identification of a neural stem cell in the adult mammalian central nervous system.Cell.1999;96(1):25-34.[6]Maguire-Zeiss KA1, Short DW, Federoff HJ.Synuclein, dopamine and oxidative stress: co-conspirators in Parkinson's disease?Brain Res Mol Brain Res.2005;134(1):18-23.[7]Jeong JO,Han JW,Kim JM,et al.Malignant tumor formation after transplantation of short-term cultured bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in experimental myocardial infarction and diabetic neuropathy.Circ Res.2011;108(11):1340-1347.[8]Li L,Xie T.Stem cell niche: structure and function.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.2005;21:605-631.[9]Van Laere AS,Nguyen M,Braunschweig M,et al.A regulatory mutation in IGF2 causes a major QTL effect on muscle growth in the pig.Nature.2003;425(6960):832-836.[10]Sugiyama T,Kohara H,Noda M,et al.Maintenance of the hematopoietic stem cell pool by CXCL12-CXCR4 chemokine signaling in bone marrow stromal cell niches.Immunity. 2006; 25(6):977-988.[11]Sacchetti B,Funari A,Michienzi S,et al.Self-renewing osteoprogenitors in bone marrow sinusoids can organize a hematopoietic microenvironment.Cell.2007;131(2):324-336.[12]Rameshwar P,Gascón P.Induction of negative hematopoietic regulators by neurokinin-A in bone marrow stroma.Blood. 1996; 88(1):98-106.[13]Pittenger MF,Mackay AM,Beck SC,et al.Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells.Science. 1999;284 (5411):143-147.[14]Rafii S,Shapiro F,Pettengell R,et al.Human bone marrow microvascular endothelial cells support long-term proliferation and differentiation of myeloid and megakaryocytic progenitors. Blood.1995;86(9):3353-3363.[15]Kacena MA,Shivdasani RA,Wilson K,et al. Megakaryocyte- osteoblast interaction revealed in mice deficient in transcription factors GATA-1 and NF-E2.J Bone Miner Res. 2004;19(4):652-660.[16]Malara A,Currao M,Gruppi C,et al.Megakaryocytes contribute to the bone marrow-matrix environment by expressing fibronectin, type IV collagen, and laminin.Stem cells. 2014; 32(4):926-937.[17]谭竞,刘霆.造血细胞三维培养体系的研究[J].中华血液学杂志, 2008,29(2):138-140.[18]Fares I,Chagraoui J,Gareau Y,et al.Cord blood expansion. Pyrimidoindole derivatives are agonists of human hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal.Science. 2014;345 (6203):1509-1512.[19]Morrison SJ,Scadden DT.The bone marrow niche for haematopoietic stem cells.Nature. 2014;505(7483):327-334.[20]Reinisch A,Thomas D,Corces MR,et al.A humanized bone marrow ossicle xenotransplantation model enables improved engraftment of healthy and leukemic human hematopoietic cells Nat Med. 2016;22(7):812-821.[21]Nicodemus GD,Bryant SJ.Cell encapsulation in biodegradable hydrogels for tissue engineering applications. Tissue Eng Part B Rev.2008;14(2):149-165.[22]Seliktar D.Designing cell-compatible hydrogels for biomedical applications.Science. 2012;336(6085):1124-1128.[23]Cushing MC,Anseth KS.Materials science.Hydrogel cell cultures. Science.2007;316(5828):1133-1134.[24]Shi M,Hu LP,Zhang XB,et al.Effects of catalase on the engraftment of human hematopoietic stem cells in NOD/SCID mice.Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2015;23(1): 183-189.[25]Reinisch A,Etchart N,Thomas D,et al.Epigenetic and in vivo comparison of diverse MSC sources reveals an endochondral signature for human hematopoietic niche formation. Blood. 2015;125(2):249-260.[26]Kubo A,Shinozaki K,Shannon JM,et al.Development of definitive endoderm from embryonic stem cells in culture. Development. 2004;131(7):1651-1662. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Hou Jingying, Yu Menglei, Guo Tianzhu, Long Huibao, Wu Hao. Hypoxia preconditioning promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells survival and vascularization through the activation of HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [5] | Shi Yangyang, Qin Yingfei, Wu Fuling, He Xiao, Zhang Xuejing. Pretreatment of placental mesenchymal stem cells to prevent bronchiolitis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 991-995. |
| [6] | Liang Xueqi, Guo Lijiao, Chen Hejie, Wu Jie, Sun Yaqi, Xing Zhikun, Zou Hailiang, Chen Xueling, Wu Xiangwei. Alveolar echinococcosis protoscolices inhibits the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into fibroblasts [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 996-1001. |
| [7] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [8] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [9] | Lun Zhigang, Jin Jing, Wang Tianyan, Li Aimin. Effect of peroxiredoxin 6 on proliferation and differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into neural lineage in vitro [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1014-1018. |
| [10] | Zhu Xuefen, Huang Cheng, Ding Jian, Dai Yongping, Liu Yuanbing, Le Lixiang, Wang Liangliang, Yang Jiandong. Mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into functional neurons induced by glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1019-1025. |
| [11] | Duan Liyun, Cao Xiaocang. Human placenta mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles regulate collagen deposition in intestinal mucosa of mice with colitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1026-1031. |
| [12] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [13] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [14] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| [15] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||